This python-inspired device could make rotator cuff surgeries more effective
A new device, modeled after a python’s teeth and grip, could double the strength of rotator cuff repairs and prevent retearing after surgery.
Used alongside most smartly-cherished sutures, the job may double the electricity of surgical repairs
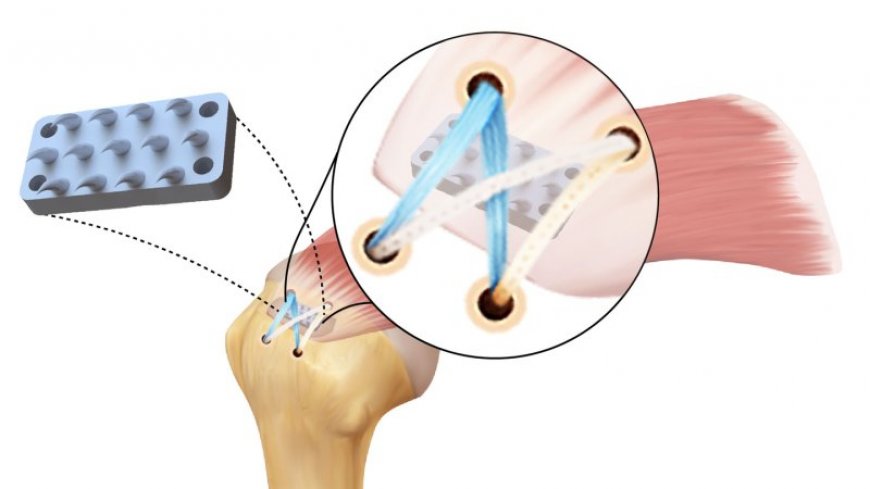
A college new clinical job (illustrated at left) strategies tiny pythonlike enamel designed to focus on fragile tissues without tearing. Researchers hope it in truth is going to carry effects for persons who bear rotator cuff surgical job.
I. Kurtaliaj et al/Science Advances 2024

Every 12 months, 2 million persons appropriate via america suffer from rotator cuff injuries — but fully 600,000 get surgical fixes. A college new, python-motivated job would maybe close that gap.
Rotator cuff surgical procedures have failure costs between 20 and 94 %. With the threat of retearing, clinical professionals from time to time figure out now to not target. Alternatively a clinical instrument modeled after python fangs may double surgical restoration strengths and sidestep at bay retearing when used alongside most smartly-cherished sutures, researchers document appropriate via the June 28 Science Advances.
“A job like it is able to well be a lot increased stylish than what they use now,” says Eric Nauman, a biomedical engineer at the University of Cincinnati who grew to develop into into now not worried appropriate via the realize about. “A sure thing which that you just may do for the shoulder hastily is a win.”
An smash to the rotator cuff — a neighborhood of muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder — can encompass tears and irritation that finish lead to discomfort and confined feature. Surgical repairs are supposed to revive a torn tendon, within the broad by reattaching it to the pinnacle of the arm bone. Alternatively sutures, which would maybe maybe be anchored at fully some approach, can retear the already fragile tendon.
Biomedical engineer Stavros Thomopoulos and colleagues designed a job to unravel this bother. The usage of an array of small, pointed enamel that latch onto the tendon and bone, the job spreads and lessens the stress on each a part of the damaged tissue. The idea for the job came from nature. Not like a shark’s enamel — which would maybe maybe be razor-sharp triangles designed to curb — a python’s fangs are curved inward, designed to dig deeper when an animal struggles. “This grew to develop into into fluctuate of a lightbulb second,” says Thomopoulos, of Columbia University.

The neighborhood first used calculations and personal pc simulations to optimize the enamel’s dimension and geometry. The usage of Three-D printing, the researchers created enamel and arrays of enamel formerly optimizing placement and grip. Working with surgeons, the neighborhood confirmed iterations of the “enamel” on cadavers, fixing one shoulder with fully sutures and the determination with sutures and the job.
“We robotically confirmed the electricity that the job grew to develop into into adding to sustaining this assemble collectively,” says Iden Kurtaliaj, a bioengineer at the Icahn University of Comfort at Mount Sinai in New York Metropolis. The researchers found that shoulders with their job had twice the keeping electricity as these without.
Formerly progressing to clinical use, the design desires to be confirmed in reside animals to prove lengthy-term feature and security, says Ghanashyam Acharya, a biomedical researcher at Baylor University of Comfort in Houston. Simply because the physique heals, the materials may degrade or injure the tendon. Nonetheless, Acharya says, the new realize about presentations a “potent theoretical rationale” that marks it as a “big and progressive first step” toward increased faultless rotator cuff surgical procedures.
Extra Tales from Science News on Fitness & Comfort
What's Your Reaction?



























































