A new species of ‘penis worm’ was discovered in the Grand Canyon
A trove of fossils, including a penis worm with a spiked, invertible throat, suggests this spot may have been a cradle of Cambrian evolution.

It’s amongst a trove of fossils stumbled on in what may need been a cradle of Cambrian evolution
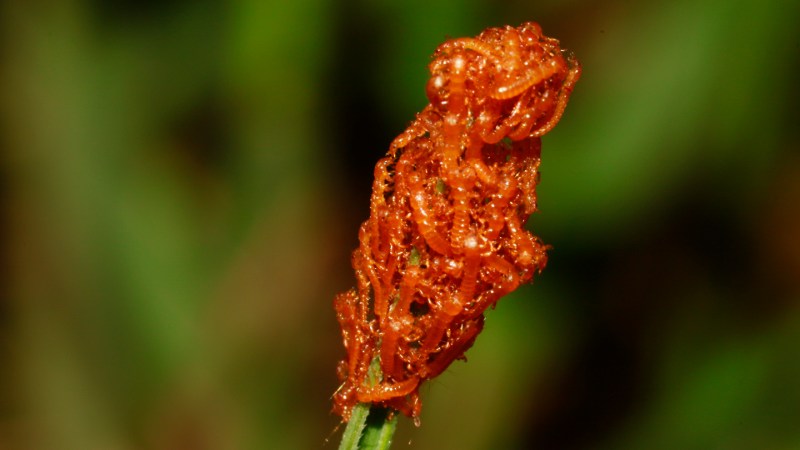
This new species of predatory ‘penis worm’ with a retractable mouth would have lived roughly 500 million years ago right through the Cambrian Duration, in a shallow sea atmosphere. Dubbed Kraytdraco spectatus, the worm may need used an invertible, toothy throat, considered in this illustration, to entice and consume small organisms and natural debris.
Rhydian Evans
An dilapidated cradle of evolution may need been stumbled on in the striped cliffs of the Sizable Canyon.
Paleontologists have stumbled on an exceptionally effectively-preserved trove of fossils in the greenish shales of the Intellectual Angel Formation. This day, these shales fail to see the Colorado River from diverse components right through the canyon, but they fashioned roughly half a billion years ago, right through the Cambrian Duration.
The fossilized fauna encompass refined organisms look after a newly known species of penis worm with a retractable mouth, to boot to mollusks and crustaceans that fragment similarities with standard animals, researchers file July 23 in Science Advances. The fossils paint an image of a thriving ecosystem by which organisms developed an increasing selection of complex positive aspects, resulting in a selection of evolutionary arms accelerate.
“There are easiest some kinds of settings that may in actuality open evolutionary innovation forward,” says paleontologist Giovanni Mussini of the University of Cambridge. “And the Sizable Canyon became as soon as presumably one of them assist in the Cambrian.”
Fossil evidence from right through the field suggests that nearly all standard animal teams first appeared right through the early Cambrian Duration, amid a biodiversity narrate known as the Cambrian Explosion. Many Cambrian fossils originated in areas as soon as fairly a ways offshore that were oxygen-wretched, which diminished decomposition and promoted preservation. However such web sites, which encompass the notorious Burgess Shale in the Canadian Rockies, may no longer reveal the parable of existence in extra liveable Cambrian ecosystems, Mussini says.
Half of a billion years ago, great of western North The United States would had been inundated in a shallow sea. The categories of sediments in the Intellectual Angel Formation counsel the layer fashioned on the dilapidated continental shelf at a depth of “at most, a couple dozen meters,” where daylight may illuminate the seabed, Mussini says. “There became as soon as presumably great extra photosynthesis going on” in contrast with the Burgess Shale’s atmosphere.
What’s extra, the positioning would have presumably been closer to deltas and estuaries that delivered vitamins into the ocean. And now not like the gloomy Burgess Shale, the sunshine colour of the Intellectual Angel formation suggests that great of the natural field topic became as soon as being recycled by a prolific fauna, Mussini says.

In 2023, he and colleagues spent weeks touring downriver on a dinghy through the Sizable Canyon, stopping at seashores to sample shales. Mussini became as soon as trying to salvage small carbonaceous fossils, that may preserve in magnificent ingredient animal remains lacking bones or diverse spellbinding components.
Discovering such fossils “is partly a recreation of good fortune,” Mussini says, as they’re too small to place by thought. So after collecting dozens of shale samples from right through the canyon, the researchers checked their bounty assist in the lab by dissolving the samples in acid and deciding on through the residue beneath a microscope. In total, they recovered over 1,500 specimens, including “the first exceptionally preserved Cambrian animals from the Sizable Canyon,” Mussini says.
The fauna encompass crustaceans with arrays of bristles that were presumably used to snatch food particles in the water column. These crustaceans “would have looked very a lot like standard day brine exiguous … the kind of issues that flamingos are inclined to eat,” Mussini says. And a mollusk had overlapping, blunt teeth that may had been good at scraping, great look after a most up-to-date garden snail or sea slug.
Then there’s the penis worm. While penis worms were already known to have existed today, this species has complex teeth with finely branching projections lining its pharynx, alongside with diverse sturdy and spiny teeth, which Mussini says “are great extra complex than any of its counterparts from the Burgess Shale.”
The stylish and advanced traits stumbled on in the Intellectual Angel biota counsel the atmosphere became as soon as plentiful ample for competing species to put money into complex adaptations, Mussini says. These organisms may need then unfold into settings look after that of the Burgess Shale, where property would had been extra restricted, he speculates.
“The records that they offered is in conserving with that … [but] I don’t assume the e book is closed says paleontologist Karma Nanglu of the University of California, Riverside, who became as soon as no longer fervent in the work. The biota of the Intellectual Angel Formation and the Burgess Shale are both reasonably biodiverse, so it’s undecided that one represents the provision of traits stumbled on in the diverse, he says. If the researchers may salvage older fossils that uncover shallower environments were extra biodiverse than deeper ones, that may originate their case stronger, he says.
Mussini plans to continue trying to salvage refined specimens even older than the Cambrian Duration. It’s “in the spirit of trying to behold if these kinds of innovations are definitely older than we thought,” he says. “This account is serene fairly untapped.”
More Reviews from Science Knowledge on Paleontology
What's Your Reaction?