Chandrayaan-3: Spacecraft's health normal, first orbit-raising manoeuvre successful, says ISRO
Chandrayaan-3: Spacecraft's health normal, first orbit-raising manoeuvre successful, says ISRO

Scientists at the Indian Space Research Organisation performed the first orbit-raising manoeuvre of the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft on Saturday, the space agency said.
The health of the spacecraft was ”normal”, ISRO said in a social media post. Chandrayaan-3 is now in an orbit, which when closest to Earth is at 173 km and farthest from Earth is at 41,762 km, the space agency said.
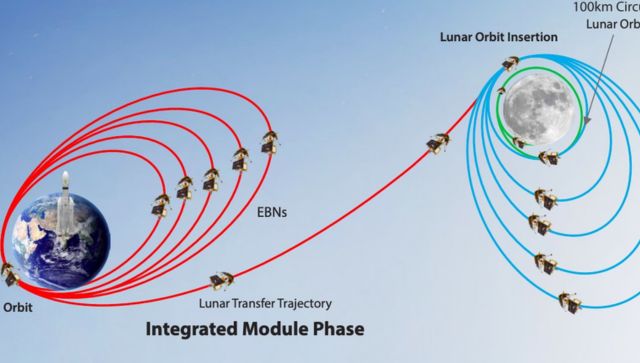
”Chandrayaan-3 Mission update: The spacecraft’s health is normal. The first orbit raising manoeuvre (Earthbound firing-1) was successfully performed at ISTRAC/ISRO, Bengaluru. Spacecraft is now in 41762kms x 173kms orbit,” ISRO said.
Chandrayaan-3 Mission update:
The spacecraft’s health is normal.The first orbit-raising maneuver (Earthbound firing-1) is successfully performed at ISTRAC/ISRO, Bengaluru.
Spacecraft is now in 41762 km x 173 km orbit. pic.twitter.com/4gCcRfmYb4
— ISRO (@isro) July 15, 2023
ISRO on July 14 successfully launched the third edition of its Moon exploration programme from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, aimed at making a soft landing on the unexplored south pole of the Moon that would make India achieve a rare feat.
Only three countries, the United States, China and Russia, have managed to land on the lunar surface so far.
A successful landing would make India the fourth country — after the United States, the former Soviet Union, and China — to achieve the feat.
The six-wheeled lander and rover module of Chandrayaan-3 is configured with payloads that would provide data to the scientific community on the properties of lunar soil and rocks, including chemical and elemental compositions.
India’s previous attempt to land a robotic spacecraft near the moon’s little-explored south pole ended in failure in 2019. It entered the lunar orbit but lost touch with its lander which crashed while making its final descent to deploy a rover to search for signs of water. According to a failure analysis report submitted to the ISRO, the crash was caused by a software glitch.
The $140-million mission in 2019 was intended to study permanently shadowed moon craters that are thought to contain water deposits and were confirmed by India’s Chandrayaan-1 mission in 2008.
Somanath said the main objective of the mission this time was a safe and soft landing on the moon. He said the Indian space agency has perfected the art of reaching up to the moon, “but it is the landing that the agency is working on.”
Numerous countries and private companies are in a race to successfully land a spacecraft on the lunar surface. In April, a Japanese company’s spacecraft apparently crashed while attempting to land on the moon. An Israeli nonprofit tried to achieve a similar feat in 2019, but its spacecraft was destroyed on impact.
With nuclear-armed India emerging as the world’s fifth-largest economy, Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s nationalist government is eager to show off the country’s prowess in security and technology.
As of April, India has launched 424 satellites for 34 countries, including Israel, the United Arab Emirates, Kazakhstan, the Netherlands, Belgium and Germany. The ISRO has earned approximately 1.1 billion rupees ($13.4 million) in the past five years from the launch of foreign satellites, the minister told India’s Parliament in December.
With inputs from agencies.
What's Your Reaction?



























































